Whether it is a portable one or a complete home theater, a digital projector isn’t a stranger to technology. As much as you would think they aren’t used as much as other appliances due to their limited array of use, there is still plenty of mechanisms that will leave you completely baffled.
As there is much more than simply light passing through different lenses to project an image across the room.
Types of projectors
To catch a fish you have to think like a fish, and for you to understand every nit bit of such complex machinery, dissecting every part of it is necessary for you to get a grip on how does a digital projector works.
Inside a projector, there is special machinery used that divides the category of digital projectors into three types.
- LCD
- Digital light processing projector ( DLP)
- LCOS
LCD projector or Liquid crystal display Projector
These are the oldest type of projector, they aren’t known for being lightweight and hence have a lower portability ratio, but tend to have an upper hand over DLP projectors due to better picture quality.

The mechanism behind an LCD projector relies on a metal halide lamp that throws countless rays which are then passed through some mirrors that splits these rays into 3 colors, red, blue, and green or better known as RGB.
This trio of RGB colors is then passed through a prism that conveys the colors onto a projector screen to display your favorite tv show, games, or simply a presentation.
Digital light processing (DLP) projector
These are the latest form of projectors that are not only cost-effective but are also highly portable. These have digital micromirrors devices (DMD) engineered into them which diverge the flood of rays thrown from a lamp light source and converge light from a spinning color wheel onto a projector screen to display your images or videos.
DLP has the upper hand of display true blacks and true whites, which is a feature rather missing in a traditional LCD projector, and oftentimes you might see brighter image quality as compared to an LCD projector.
LCOS Projector or Liquid crystal on silicon Projector
Not only do they have the most complex technology built into them, but require a pretty penny. But as technology and the industrial revolution is moving forward, things have started to look favorable in terms of price cost as manufacturers have started Budget LCOS projector to cover all sort of consumer and their demands.
Liquid crystal technology on silicon or LCOS is a better and upgraded form of DLP and LCD projectors which has richer picture quality as well as no rainbow effect which you might often see in DLP projectors.
Although often regarded as a hybrid, it is much more than that because it does the job much better than the latter by combining the technology of both LCD and DLP projectors without having any disadvantages of the technologies mentioned above without having the need for a spinning color wheel.
Because it comes with a unique 3-chip technology that delivers a trio of blue, green, and red colors all at once and combines it to project its imagery which is much larger than a DLP projector.
However, since there is a lot of hardware involved that processes the light and display on a projector screen, things tend to get a little heavy which cuts on the portability ratio and which is why DLP projectors are better considered in terms of being lightweight as compared to a liquid crystal technology on silicon projectors.
Want to know How Does a Digital Projector Work?
Now it’s time to discuss the working principle of all three types of projectors i.e. LCD, DLP, and LCOS so that you can get a better understanding of this machinery.
How LCD projectors work
To understand the working principle you need to know the components of LCD projectors which are given below.
Components of LCD technology:
-Lamp.
-2 Dichroic mirrors.
-LCD panels.
-Dichroic prism.
-Lens.
Working principle of LCD projectors
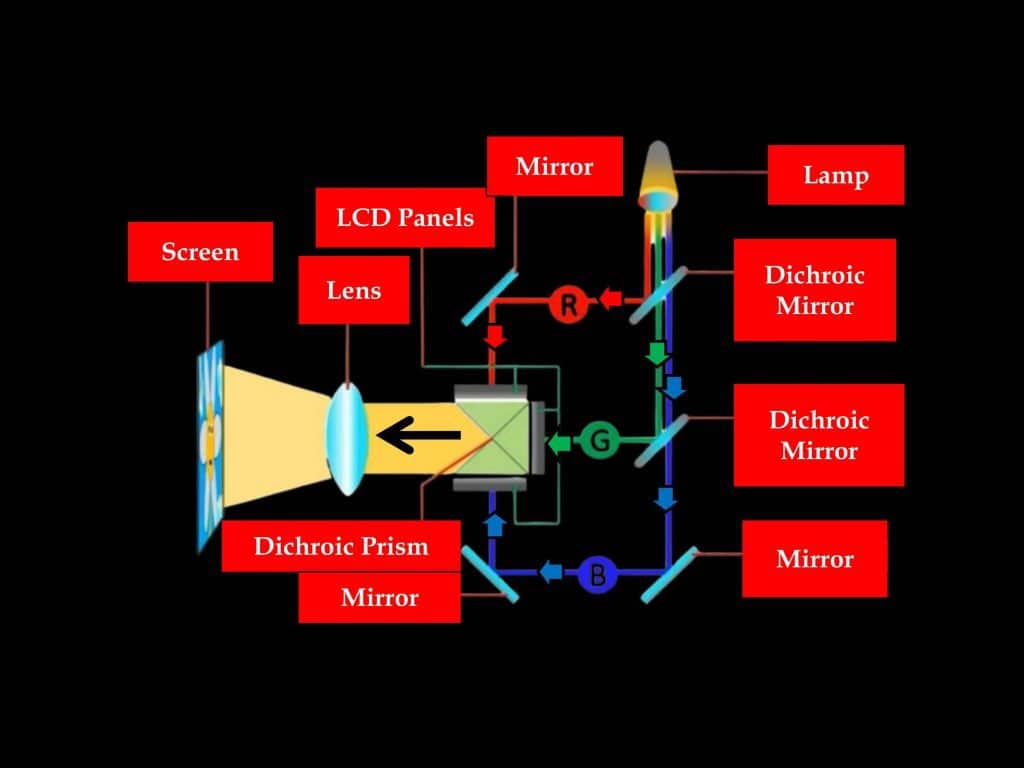
Now that you know the components, it’s time to understand the working principle which is as follows.
The light produced by a lamp is first passed through a dichroic mirror that reflects some light and allows some to pass. The reflected lights become red because this dichroic mirror only reflects those lights that have a wavelength of red. Then these lights are passed on to a mirror which then reflects the lights on an LCD panel.
what is the purpose of LCD panel in LCD projector?
LCD panels actually modulate and control the amount of light that is being passed. This is done with the help of liquid crystals that are present in these LCD panels because when an electric field is applied to these liquid crystals, they actually change their alignment.
And when this happens, it actually allows more or less light to pass through it. So, when the electric field is turned on, more light is allowed to pass and when it’s turned off, less light is allowed to pass.
On the other hand, the lights that were allowed to pass through the first dichroic mirror are then again subjected to a second dichroic mirror which reflects green lights on an LCD panel, and only blue lights are allowed to pass. These blue lights are then reflected by mirrors and pass through an LCD panel.
Finally, all these lights that have been reflected by different mirrors and passed through different LCD panels are then united by a dichroic prism. Then it projects images through the lens.
How DLP projectors work
As we have mentioned before, we need to know the components first. So, let’s see these:
Components of DLP technology:
-Laser diode.
-Dichroic mirror.
-Phosphor wheel.
-Mirrors.
-Color wheel.
-DMD chip.
-Prism.
-Projection lens.
Working principle of DLP projectors:
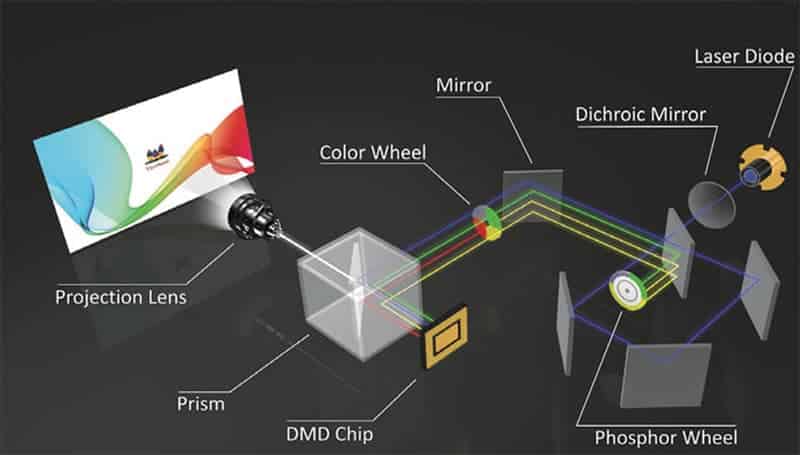
These types of projectors use a technology called a digital micromirror device or DMD. This is a chip that has an array of tiny mirrors on it and a laser diode is used as a light source in DLP projectors.
This light from the laser diode first hits a dichroic mirror. A dichroic mirror is a type of filter that only allows certain wavelengths of light to pass through it.
The wavelengths of light that are allowed to pass through the dichroic mirror are then sent to a phosphor wheel. Some lights pass through the wheel while some lights reflect off of it.
The light that passes through the wheel hits a mirror. This mirror reflects the light onto the color wheel. The color wheel is a spinning disc that has different colors on it. Which converts the lights into red, green, and blue colors.
And the reflected lights become yellow because of the phosphor wheel. These lights also go through the color wheel but they stay yellow and then they along with RGB lights are reflected off of a mirror. This mirror reflects the light onto the DMD chip.
The DMD chip is made up of millions of tiny mirrors. Each mirror represents a pixel on the screen. The angle of each mirror can be adjusted. The light that hits the DMD chip is reflected off of the mirrors and onto the prism.
The prism is a piece of glass that has 3 sides. The first side of the prism reflects the light onto the second side. The second side of the prism reflects the light back to the first side. And then it is reflected off of the first side and out of the projector through the lens and you get the projected images.
How LCOS projectors work
It’s time for our last projector-type LCOS projector. As before let’s know the components first.
Components of LCOS technology:
-Lamp.
-LCOS panels.
-Prisms.
Working principle of LCOS projectors
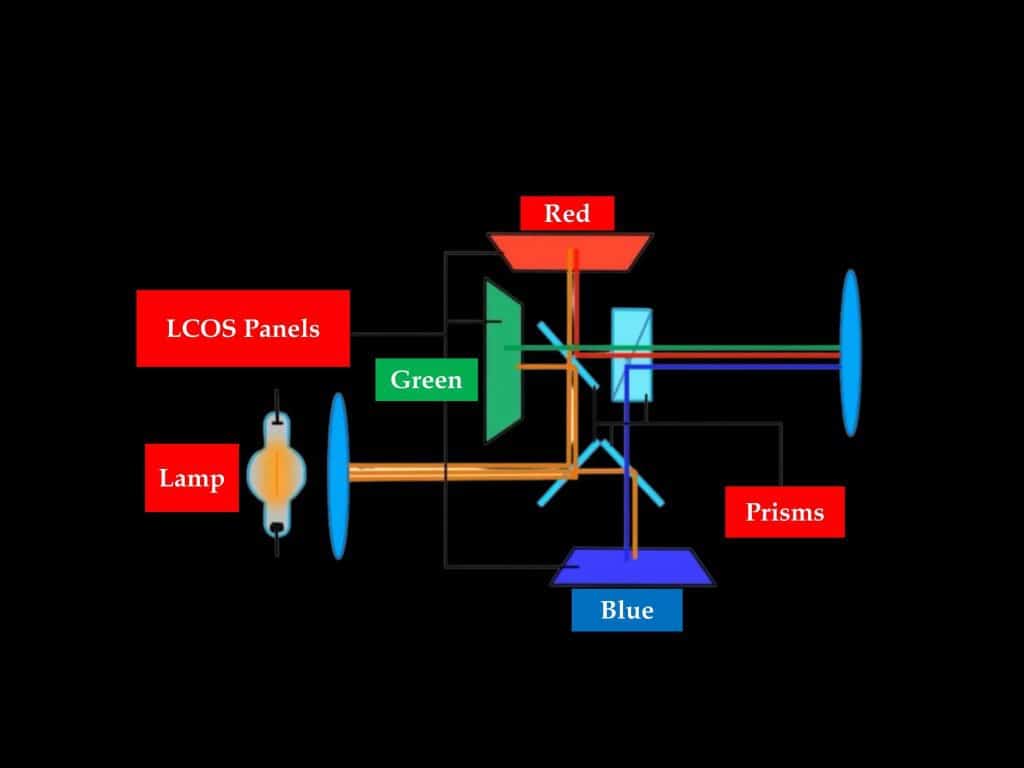
LCOS projectors are the type of projectors that uses a technology called liquid crystal on silicon or LCOS. the lamp is used as a light source in these projectors.
The lights from the lamp firstly fall on prism mirrors. From there the lights go on different LCOS panels and create RGB color lights. This RGB lights then enter another prism and create images through the lens.
Attributes of a projector
A projector has many other features that differentiate it from one another, although these attributes differ on the basis of manufacturer and price point, most of them have the same principles and features.
- Aspect ratio
- Resolution size
- Throw distance
- Lumen brightness
- Interfaces
- Contrast ratio
These are the attributes that make a projector a whole and all of these technologies have a great deal of impact on the output of these attributes.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions regarding projectors and projectors that might be of interest to you.
Q: What are the benefits of a digital projector?
A: the benefits of a digital projector are numerous. The main benefit is the ability to make a much larger screen and it is much brighter than a traditional projector.
Q: What is the difference between a traditional projector and a digital projector?
A: A traditional projector is one that has a spinning color wheel. The light shines through the color wheel and a prism reflects the light onto a screen. A digital projector uses an LCD panel and a digital chip to deliver the image.
Q: Do I need to buy a tripod for my projector?
A: Yes, you will need a tripod if you are using a projector that has a lens that is not mounted on a stand. The tripod allows you to hold the projector up to your ceiling or wall so that the light shines through the lens
Q: What makes 3d and 2d projectors different from each other?
A: A 3D projector uses a special lens to deliver the image to the screen, which is a bit like a pair of binoculars. This is important because it allows you to project the image onto the screen from all angles. A 2d Projectors, on the other hand, only project the image onto the screen from one angle. This means that you can’t watch the image from the side or from above the projector.
Conclusion
Knowledge is power and after reading this article you now have the power to invest in a better option with a quality price-to-value ratio as now know how a digital projector works. Hope this article has been plenty beneficial for you and if you are an individual that was looking to invest in home theater, I hope this guide has paved your way and saved you precious time.
Feel free to comment below if you have any queries or any sort of problem, I will be much obliged to sort you out.

